Powered by awesome Binder: https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/baking-bad/pytezos/binder?filepath=michelson_quickstart.ipynb
- Get the latest image from dockerhub (only when new releases are published)
docker pull bakingbad/michelson-kernel
- Create container using verified docker image:
docker run --rm -it -p 127.0.0.1:8888:8888 -v $(pwd):/home/jupyter/notebooks bakingbad/michelson-kernel
- Open the link from container output in your browser
- Save notebooks in the mapped folder in order not to loose them
- Requires Python 3.7+. The recomended way to install it (especially if you plan to use multiple versions) is pyenv. Make sure you have all necessary packets installed. After that:
pyenv install 3.7.0
pyenv local 3.7.0 # per folder
pyenv global 3.7.9 # per system
- Ensure you have several crypto libraries installed (see pytezos docs):
sudo apt install libsodium-dev libsecp256k1-dev libgmp-dev
- Install the PyTezos package using pip
pip install pytezos
- Install Jupyter
pip install jupyter
- Install Michelson kernel
michelson-kernel install
- Check that Jupyter is now supporting Michelson kernel
jupyter kernelspec list
- Run jupyter
jupyter notebook
Open the link from the command output, create new notebook with Michelson kernel.
- Follow steps 1-2 from "Option 3" to ensure you have correct Python version and packets required for the PyTezos library
- Ensure the following packages are installed:
libssl-dev zlib1g-dev uuid-dev - Ensure you have
poetryinstalled - Get the sources, build and install
git clone https://github.com/baking-bad/pytezos
cd pytezos
poetry install
- Follow steps 4-6 from "Option 3"
- Run the following command
jupyter kernelspec uninstall michelson -f
- Check that Jupyter is no longer supporting Michelson kernel
jupyter kernelspec list
- Uninstall Python package
pip uninstall pytezos
- Technical details of the REPL implementation
https://forum.tezosagora.org/t/michelson-repl-in-a-jupyter-notebook/1749 - Interactive tutorial demonstrating REPL features
https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/baking-bad/pytezos/binder?filepath=michelson_quickstart.ipynb - Same, but a rendered version
https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/baking-bad/pytezos/blob/binder/michelson_quickstart.ipynb
Located in the current repository:
https://github.com/baking-bad/pytezos/tree/master/notebooks
These instructions are not Michelson primitives and thus cannot be used outside of the Jupyter.
In the Jupyter editor helpers are highlighted in blue.
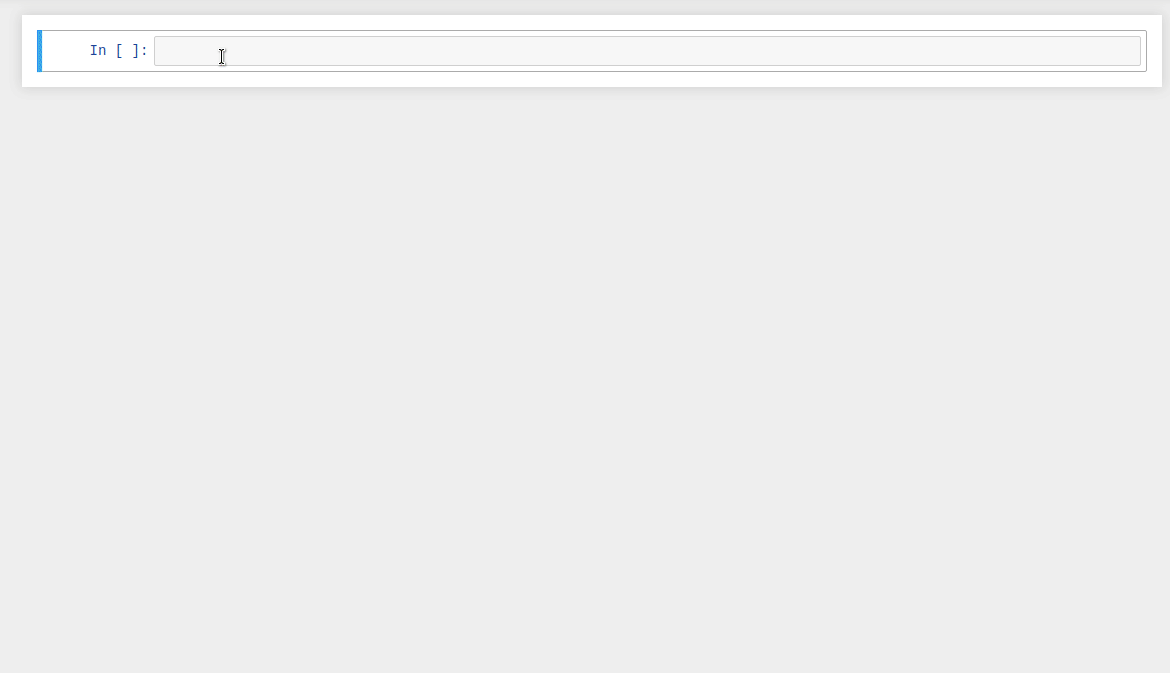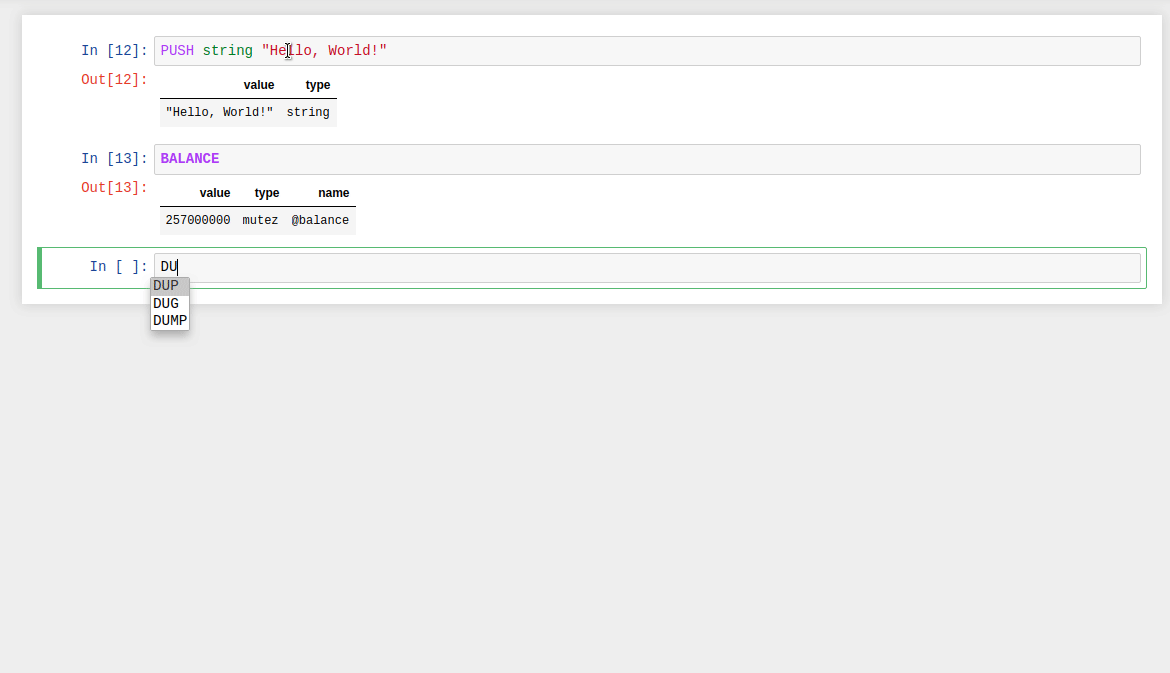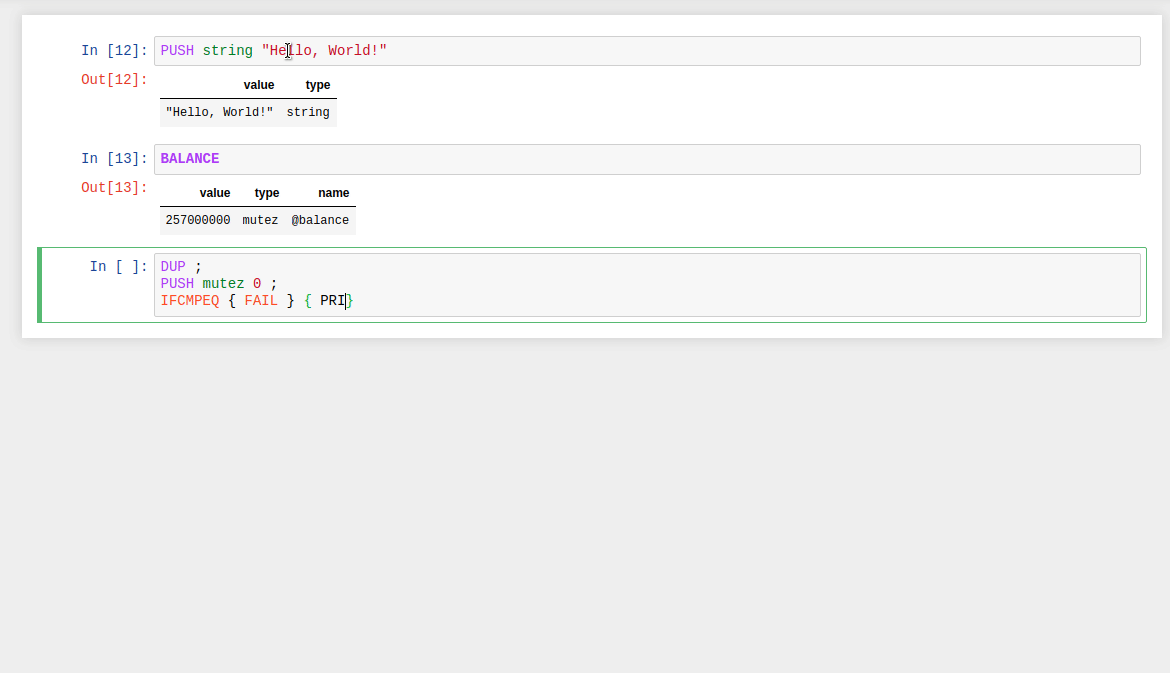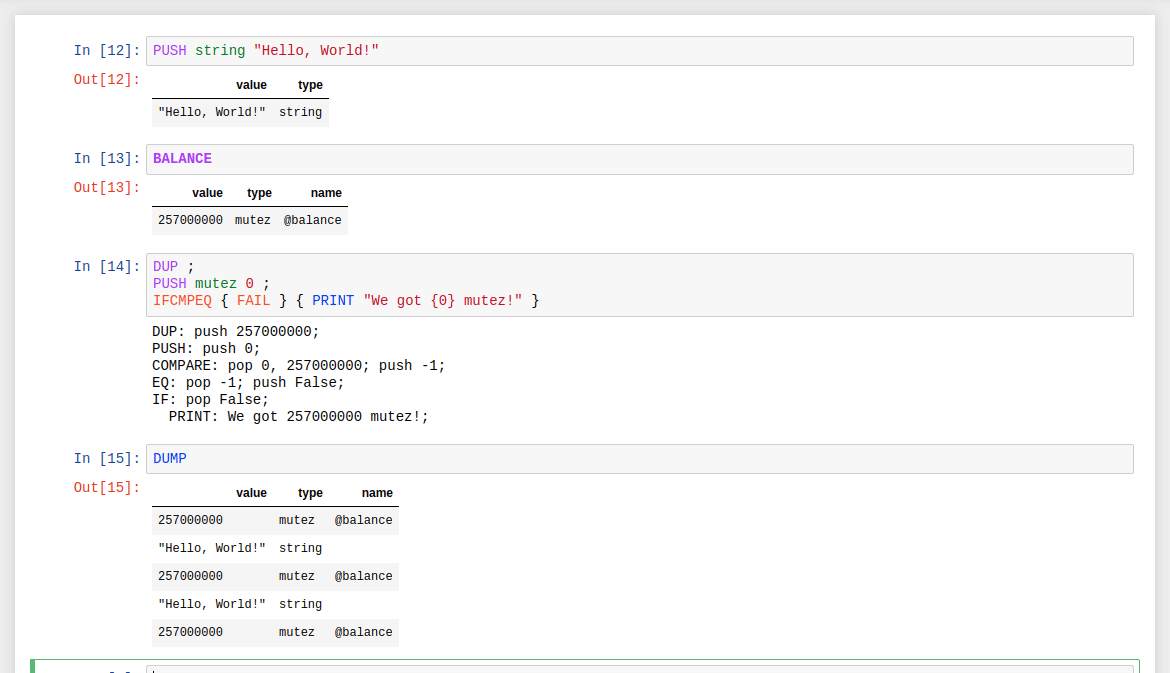
Returns the whole stack with values, types, and annotations if any.
Returns top n items from the stack.
Prints a formatted string to the stdout, referencing arbitrary stack elements is allowed:
PRINT "This is the top element {0}, and this is the second {1}"
Clears the stack.
Expands Michelson macros:
EXPAND { PAPAIIR }
Loads Michelson source from the filesystem (absolute or relative path) INCLUDE "test.tz", or from one of the Tezos networks INCLUDE "mainnet:KT1VG2WtYdSWz5E7chTeAdDPZNy2MpP8pTfL". Initializes parameter, storage, and code sections. If loaded from the network, current storage is also written to the STORAGE variable and can be accessed later.
Sets value for on of the context-dependent Michelson instructions: AMOUNT, BALANCE, NOW, SOURCE, SENDER, CHAIN_ID.
Enables or disables verbose output: DEBUG False or DEBUG True.
Takes the top of the stack, searches for temporary big_map instances in that element, and displays what the big_map_diff would be like if it was a contract execution ending.
Simulates the contract execution beginning. Requires parameter and storage sections initialized. Also, clears the stack.
The %entrypoint argument can be omitted, %default will be used in that case.
This helper also allocates temporary big_map instances if any in parameters or storage.
You can use STORAGE variable for the storage_expr, in case you have previously loaded it from the network.
Simulates the contract execution ending. Requires a Pair of operation list and valid storage on top of the stack. Returns a list of internal operations, new storage, and big_map_diff.
Clears the stack, deletes all big_map instances.
Does the same as the version without parameters, but also initializes NETWORK and CHAIN_ID variables.
Can be used to set real network context in order to access blockchain data.
Requires code section initializes. Internally calls BEGIN, then executes code, and finishes with COMMIT.