A Rhino/Grasshopper plugin allowing the CityJSON format to be directly used in Rhino 3D and Grasshopper without the loss of semantic information. The primary focus of the plugin was to function on the 3D BAG data. However, the plugin functions as well with other CityJSON files. The plugin consists out of multiple Grasshopper components exposing data in a format that is directly usable in grasshopper, and allows all this data to be baked into Rhino.
Currently only supports CityJSON 1.1 and 1.2.
- 3D BAG does not include all the data the Normal bag has included.
- Template handling is untested.
- Material importing can be extremely slow (This sadly is an issue with Rhino).
- Textures are not supported.
- Rhino data can not be exported to the CityJSON format.
This is the easiest and recommended way to install the plugin. However newer features/updates will be released via this outlet only when deemed completely stable and finished. This means that less versions will be available and experimental features will not be available. For these the plugin has to be accessed via this GitHub page.
Access the plugin manager by typing "PackageManager" in the rhino command prompt. This will open the Package manager. In the package manager search for RhinoCityJSON (make sure no spaces are present between the words). Select the plugin, select the desired version and press install. After restarting Rhino the plugin will function.
URL: https://www.food4rhino.com/en/app/rhinocityjson
Before the integration of the package manager Food4Rhino was the primary source to acquire the plugin from. The package manager install, example files and the old .gh files can be accessed from here.
Similar to the package manager newer features/updates will be released via that outlet only when deemed completely stable and finished. This means that less versions will be available and experimental features will not be available. For these the plugin has to be accessed via this GitHub page.
More regularly updated GHA components are available from this github page. These can be found in the "dist" folder. Note that, although these components are more up to date, they also are possibly experimental, unfinished and unstable.
If it is desired to edit the code it is possible to compile the code yourself. If working with Visual Studio loading the RhinoCityJSON.sln should automatically resolve most of the issues. However, the build output path has to be set to function correctly. It is recommended to set this to the Grasshopper component directory path, or a subfolder of the Grasshopper component directory path. This path can be easily found by opening Grasshopper, going to File->Special Folders->Component Folder.
A simple summary of the plugin's component.
The Reader Objects processes all the object data supplied by a CityJSON file.
Inputs:
- Path. A path to a CityJSON file. Multiple file paths are optional, based on the data stored in the file they will be placed correctly related to each other.
- Activate. A Boolean dictating if the component is active or not.
- Settings. A settings object that can be supplied by the Settings component.
Outputs:
- Geometry. A list of single surface Breps.
- Surface Information. Information 1:1 related to the surfaces that are output by the geometry output.
- Object Information. Information related to the objects.
The Reader Template processes all the template data supplied by a CityJSON file. The Geometry and Surface Information output are related to the templates while the Object data is related to the objects that use the templates. This data can be baked directly to rhino with the Template Bakery. To cast all the data to represent the objects use the Template2Object component. This will allow the user to easily modify the data in grasshopper however it will lose the template knowledge.
Inputs:
- Path. A path to a CityJSON file. Multiple file paths are optional, based on the data stored in the file they will be placed correctly related to each other.
- Activate. A Boolean dictating if the component is active or not.
- Settings. A settings object that can be supplied by the Settings component.
Outputs:
- Template Geometry. A list of single surface Breps representing the templates.
- Surface Information. Information 1:1 related to the surfaces that are output by the geometry output.
- Object Information. Information related to the objects that utilize the templates.
Fetches the Metadata, Textures and Materials from a CityJSON file.
Inputs:
- Path. A path to a CityJSON file. Multiple file paths are optional, based on the data stored in the file they will be placed correctly related to each other.
- Activate. A Boolean dictating if the component is active or not.
- Settings. A settings object that can be supplied by the Settings component.
Outputs:
- Metadata Information. Generic metadata output.
- LoD. the stored LoD levels.
- Materials. The materials that are stored in the file.
- Domain. The spatial domain that is stored in the file.
Reads the semantic city data of rhino geometry and outputs it as Merged Surface Information.
Inputs:
- Geometry. The geometry that is stored in a Rhino file. Make sure the semantic data related to an object is properly stored. More info on this will be coming soon. Until then it is recommended to only use geometry that has been baked by the plugin as input.
Outputs:
- Merged Surface Information. Merged and filtered information input related to the surfaces.
The Settings component gives the user more control over the Reader Object, Template and Document components.
Inputs:
- Translation. If true, the geometry will be placed in the rhino model as if the Rhino world coordinates comply 1:1 with the coordinate system that is used in the CityJSON file.
- Model Origin. If a point/coordinate is supplied this coordinate will be translated to be at the origin of the Rhino model (0,0,0).
- True north. If a value is supplied the geometry will be rotated around the Model Origin coordinate to comply with this True North.
- LoD. If a value is supplied only the data related to that LoD is loaded (multiple values allowed).
- Domain. Box within the objects stored in the files are loaded into grasshopper. Objects falling completely outside will be ignored.
Outputs:
- Settings. A settings object which can be fed into the Simple Reader and/or Reader component
The Bakery component is a custom baking component that will not only bake the geometry, but also the related semantic data.
Input:
- Geometry. A List with geometry that is desired to be baked.
- Merged Surface Information. Merged and filtered information input related to the surfaces. Use the Information Manager component to convert and merge the object data to surface data.
- Materials. The material output from the Reader Document output.
- Activate. A Boolean dictating if the component is active or not (Recommended to use a button to activate and not a Boolean toggle).
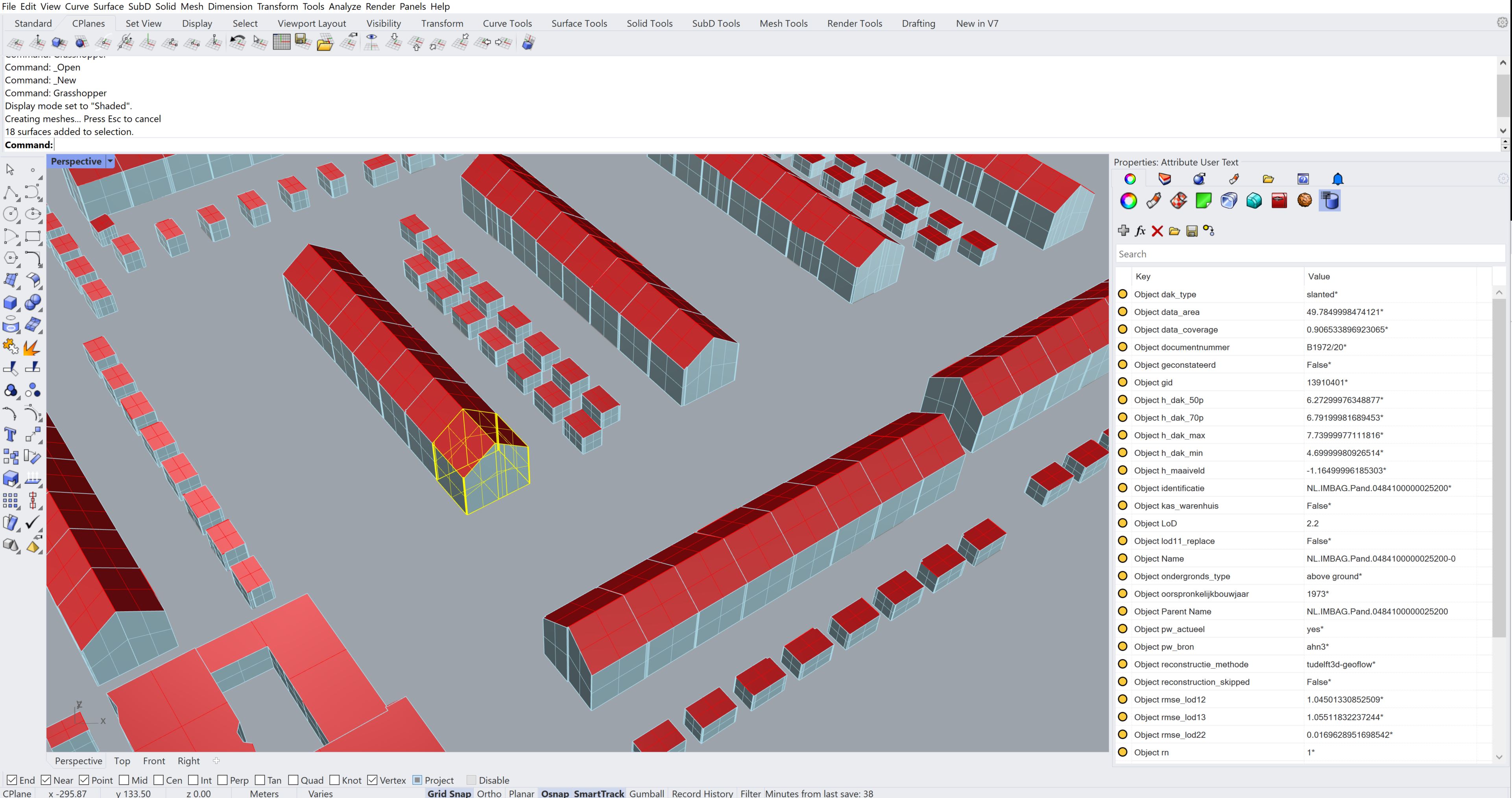
The semantic data will be stored per surface at: Properties->Object-Attribute User Text. Additionally the LoD and major object types will be used to create a hierarchy of layers. Semantic values with a * are inherited from the parent object.
The Template Bakery is a custom baking component that will not only bake the template geometry, but also place it at the correct location and include its related semantic data. Every templated object will be converted to a Rhino Block. Unlike the normal Bakery the Template Bakery does not require use of the information manager.
Input:
- Geometry. A List with template geometry that is desired to be baked.
- Surface Information. Information 1:1 related to the surfaces that are output by the geometry output.
- Object Information. Information related to the objects that utilize the templates.
- Materials. The materials related to the geometry
- Activate. A Boolean dictating if the component is active or not (Recommended to use a button to activate and not a Boolean toggle).
Each instance of a template will be placed in a block. Allowing to move, scale and rotate the objects without changing the underlying geometry. Changing the template is possible with the block edit command. Edits made in block edit mode will update every instance of that block The semantic data will be stored per surface at: Properties->Object-Attribute User Text. Additionally the LoD and major object types will be used to create a hierarchy of layers. Semantic values with a * are inherited from the parent object.
The Attribute Add component allows the user to add an attribute to the information objects related to the loaded surfaces and objects.
Input:
- Information Objects. Information objects related to the objects, surfaces or metadata.
- Attribute Name. The name/key of the new attribute (Selector will be spawn automatically).
- Attribute Value. The value of the new attribute. This is a nested value, more values per key are possible.
Output:
- Information Objects output. The updated Information list with the new attribute included.
The attribute Filter component allows the user to filter data from the information objects related to the loaded surfaces and objects.
Input:
- Information Objects. Information objects related to the objects, surfaces or metadata.
- Attribute Name. The name/key of the attribute used to be filtered (Selector will be spawn automatically).
- Attribute Value. The value which the attribute is desired to have (can be a list).
Output:
- Filtered Information Objects. The filtered object information.
Note that this component does not filter the geometry, feeding this output in the Information Manager will resolve this.
The attribute Remover component allows the user to remove an attribute from the information objects related to the loaded surfaces and objects.
Input:
- Information Objects. Information objects related to the objects, surfaces or metadata.
- Attribute Name. The name/key of the attribute that is to be removed (Selector will be spawn automatically).
Output:
- Information Objects output. The updated Information list with the attribute excluded.
The Attribute Selector exposes the value(s) of a desired attribute stored in the information objects.
- Information Objects. Information objects related to the objects, surfaces or metadata.
- Attribute Name. Attribute name of which the values are desired (Selector will be spawn automatically).
The Object Information can not be directly used by the bakery component. The Information Manager copies the data over the surfaces allowing it to be used by the bakery. The Information Manager also resolves the filtering of geometry based on the information object (both related to the surfaces and city objects) input.
Input:
- Geometry. A list of single surface Breps.
- Surface Information. Information related to the surfaces.
- Object Information. Information related to the objects.
Output:
- Geometry. (Filtered) geometry output.
- Merged Surface Information. Merged and filtered information output related to the surfaces.
The information splitter can return the merged surface information back to the normal surface information and object information.
Input:
- Merged Surface Information. Merged and filtered information input related to the surfaces.
Output:
- Surface Information. Information related to the surfaces.
- Object Information. Information related to the objects.
To ease the processing and filtering this component can create un-templated objects out of templated objects. The format of the converted objects is identical to the normal objects that are outputted by the Reader Objects component.
Input:
- Template Geometry. A list of single surface Breps representing the templates.
- Surface Information. Information 1:1 related to the surfaces that are put in the geometry output.
- Object Information. Information related to the objects that utilize the templates.
Output:
- Geometry. A list of single surface Breps representing all the templated objects as normal objects. Surface Information. Information 1:1 related to the surfaces that are output by the geometry output.
- Object Information. Information related to the objects.
The material output of the Document Reader Component is of a custom type. To display this type in grasshopper the Explode material component can be used.
Input:
- Materials. The material output from the Reader Document component.
Output:
- Name. The material name.
- Ambient Intensity. The ambient intensity.
- Diffuse Color. The diffuse color.
- Emissive Color. The emissive color.
- Specular Color. The specular color.
- Shininess. The shininess of the material.
- Transparency. The transparency of the material.
- isSmooth. Boolean defining smoothness.