Here I made a sample study on how to create a message queue system with "RabbitMQ", which is a message queue system.
RabbitMQ is an asynchronous message queuing system between communicating systems. A message is created and the generated message is accepted and transmitted to the relevant place (queue) for consumption. Our consumer tool, which constantly listens to this queue, also receives the incoming messages and sends a message to the manufacturer that the message is gone.
Written in the Erlang programming language and built on the Open Telecom Platform framework, today RabbitMQ runs on several operating systems and cloud environments and provides a range of developer tools for many popular languages.
Message Broker; is the general name given to message queue systems. RabbitMQ is just one of them. Kafka, MSMQ vs. other message queue systems.
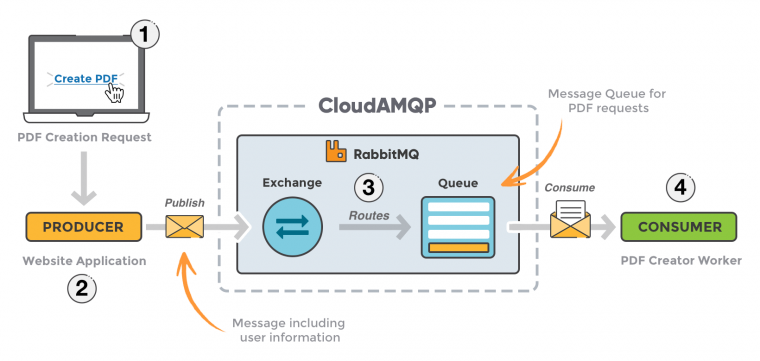
- Producer: It is the application that sends messages to the queue and generates it.
- Consumer: It is the application that processes messages by consuming the messages in the queue it listens.
- Queue: It is the list where messages are added, consumed and kept.
- Exchange: Producer does not send the message it produces directly to the receiver or queue, there is a message router in between, this is the structure that performs the forwarding process. Producer transmits the message it produces to the exchange, the exchange adds the incoming message to the queue with the relevant information, and if there is a consumer listening, it receives the next message from the queue for processing. In short, its task is to transmit the message it receives according to the specified Routing Key to the relevant Queue.There are 4 different exchange types. Direct Exchange , header exchange, fanout exchange, topic Exchange
- Binding: It is the routing rule of the connection to be established between Exchange and Queue. Exchange distributes the messages it receives to the corresponding queues according to this rule.
- Routing Key: It is the notification of the message produced by the Producer and transmitted to Exchange by marking which queue it will be routed to.
- Exhange Type: It is the type that specifies the method according to which the message will be transmitted to the queue.
- I am doing my operations using the swagger interface in a web api project.
- First, while rabbitmq is running, we make the connection process so that our manufacturer application can connect. You can check this page GitHub Pages.
- After connecting, I create an exchange called test1 of direct type.
- Then I create a queu named "testqueu".
- Then we do the bind operation to specify which queu the exchange incoming message will go to. Here we give the names of exchange , queu correctly and because we use direct, we give the name of the queu in the name of the routingkey.
- To send a message to the consumer, we send the exchange name, routing key and our message. We don't have a service listening to these yet, but these messages will already be queued and waiting in our que. This is actually one of its best advantages. When the consumer service is disabled due to an error, the messages we send will not be left unanswered and will start processing when the consumer service starts working again.
- Now I'm creating a console application to create a simple consumer service. In this application, I give the name of the queue that should connect to the rabbitmq system and listen.You can check this page GitHub Pages.
- I can't run my console application and incoming messages are written in a queue in the console application.