-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 346
Erle Rover Setup
Erle Rover is an easy-to-use platform that can be customized to work with Jetson for the purpose of autonomous navigation.
The current implementation of the rover control functionality is very simple and essentially relies on outputting PWM values using RC override MAVROS messages.
NVIDIA Jetson TX1/TX2 can be used as a companion computer with Erle Brain 3 (EB3). In this configuraiton, EB3 is used to run MAVROS only to control a vehicle (e.g. rover), the rest of the nodes are running on Jetson and ground control station (laptop).
There are 2 ways to connect Jetson and EB3:
- Connect Jetson and EB3 using Ethernet protocol. This is a more secure/reliable/faster method and should be default option. This method also allows to keep Jetson WiFi AP intact and connect to the Jetson via WiFi if needed.
- Connect Jetson to EB3 WiFi access point (AP). This is a less secure/reliable method. For example, it might be used in case Jetson carrier board does not have Ethernet port.
Here is the example of Jetson mounted on the rover:
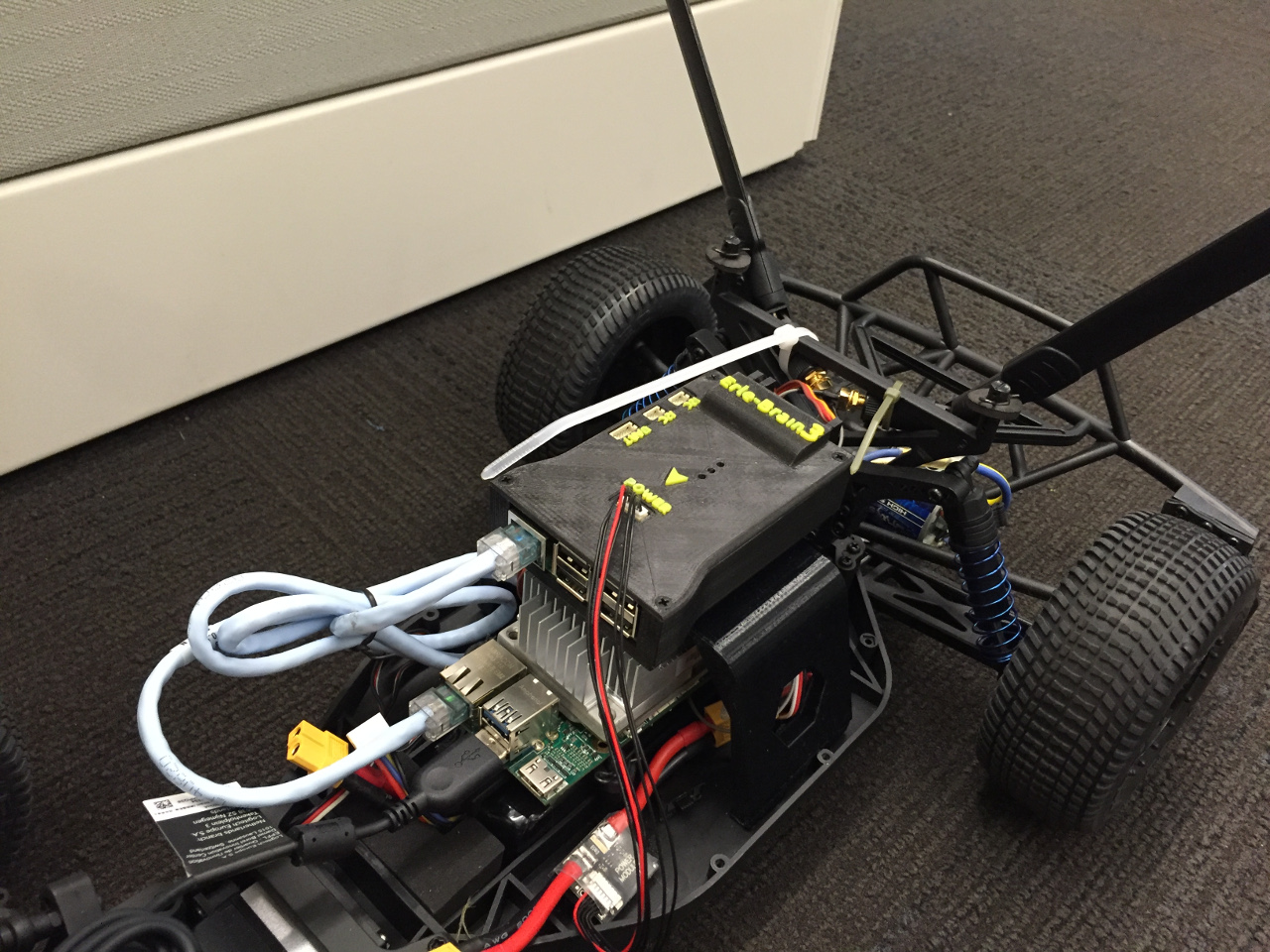
- Connect Jetson carrier board and EB3 using ordinary Ethernet cable (note: you do not need to use crossover cable, it's a thing from the past).
- Login/SSH to Jetson and change IPv4 Settings for the Ethernet connection. You need to set Method property to Shared. This can be done either in GUI or via command line:
nmcli connection modify "Wired connection 1" ipv4.method sharedRestart Jetson after making the changes. - Verify that Jetson and EB3 are connected by running
ifconfigand checking that Ethernet interface has proper IPv4 address. For Jetson board the address should be something like10.42.1.1, on EB3 side it will be something like10.42.1.86. As an additional check, make sure you can ping Jetson from EB3 and vice versa.
In case there are more nodes than just Jetson and EB3 and nodes that connect on different NICs need to communicate with each other (publish/subscribe), there is additional step that needs to be done: network routing setup. One example of such configuration can be Jetson running a ROS node that is subsribed to a topic published by another ROS node running on GCS (laptop). In such scenario, Jetson and GCS will be on different networks (Ethernet vs. WiFi) so proper routing is needed.
Note: if you just have Jetson + EB3, this step is not required.
Before making static changes to a Linux network configuration, it is a good idea to test everything by using dynamic configuration. If something does not work, rebooting will restore the previous configuration.
- Check that IP4 forwarding is enabled on EB3:
sudo sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forwardEnable if needed by running this command:sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 - Check the IP addresses of EB3, Jetson and GCS. It might be something like
10.42.1.1for Jetson,10.0.0.2for GCS and 2 addresses on EB3:10.0.0.1for WiFi interface and10.42.1.86for Ethernet. You can further verify that you cannot ping GCS from Jetson:ping 10.0.0.2(connect: Network is unreachable) and vice versa. - Setup routing on Jetson to GCS via EB3 Ethernet NIC:
sudo ip route add 10.0.0.0/24 via 10.42.1.86. - Setup routing on GCS to Jetson via EB3 WiFi NIC:
sudo ip route add 10.42.1.0/24 via 10.0.0.1 - Now check that everything is working by pinging Jetson from GCS and vice versa.
Note: your Jetson IP addresses can be different, double check by running
ifconfig
TBD, google for now
Connect Jetson to EB3 WiFi AP. You can make the Jetson to connect automatically by modifying network interface file (google for more info).
Note that by default EB3 allows only one client, if you need more then modify DNS Masquerading configuration file located at /etc/dnsmasq.conf. Refer to DNSMASQ documentation for more details.
- Set the ROS master env variable on every machine except EB3, using appropriate IP. For example, on Jetson it can be:
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://10.42.1.86:11311while on GCS:export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://10.0.0.1:11311 - Set
ROS_IPenv variable on every client including EB3, using appropriate IP. For example, on Jetson it can be:export ROS_IP=10.42.1.1while on GCS:export ROS_IP=10.0.0.2. - Restart ROS and MAVROS. Since our setup requires only MAVROS, below are the commands to restart MAVROS:
sudo systemctl stop mavros.service
sudo systemctl stop ros.service
roscore &
rosrun mavros mavros_node _fcu_url:="udp://:6001@" _gcs_url:="udp://10.0.0.1:[email protected]:6000?ids=1,255,252"
- Verify that messages can be propagated between the clients by running
rostopic listand thenrostopic echo /mavros/state. If everything is setup correctly, the first command should display list of topics, while the second - start producing MAVROS state in the console. If you don't see any output from the second command - check your IP addresses and routing again. - Optional: in case you have more than just Jetson (e.g. GCS) that require message exchange, verify that it works. For example, if GCS is running joystick node with topic
/joythat is subscribed by a client running on Jetson, verify that Jetson can receive messages by running the following on Jetson:rostopic echo /joy
We created a Docker image that enables running simulations in Gazebo using Erle Rover models. Refer to the documentation on how to use it.
